Maths-
General
Easy
Question
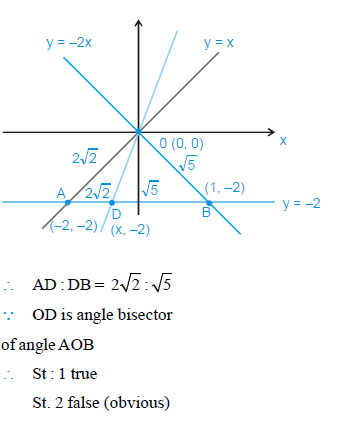
The line  and
and  intersect the line
intersect the line  at P and Q respectively. The bisector of the acute angle between L1 and L2 intersects L3 at R
at P and Q respectively. The bisector of the acute angle between L1 and L2 intersects L3 at R
Statement - 1 : The ratio PR : RQ equals 
Statement - 2 : In any triangle, bisector of an angle divides the triangle into two similar triangles.
- Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true ; Statement-2 is correct explanation for Statement-1
- Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true ; Statement-2 is not a correct explanation for Statement-1
- Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false
- Statement-1 is false, Statement-2 is true
The correct answer is: Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false
Related Questions to study
maths-
If one of the lines given by  is 3x + 4y = 0, then c equals :
is 3x + 4y = 0, then c equals :
If one of the lines given by  is 3x + 4y = 0, then c equals :
is 3x + 4y = 0, then c equals :
maths-General
maths-
If the sum of first  natural numbers is 1/5 times the sum of their squares, then the value of
natural numbers is 1/5 times the sum of their squares, then the value of  is
is
If the sum of first  natural numbers is 1/5 times the sum of their squares, then the value of
natural numbers is 1/5 times the sum of their squares, then the value of  is
is
maths-General
maths-
If  , then the value of x in terms of y is
, then the value of x in terms of y is
If  , then the value of x in terms of y is
, then the value of x in terms of y is
maths-General
maths-
Given the lines y + 2x = 3 and y + 2x = 5 cut the axes at A, B and C, D respectively.
Statement- I ABDC forms quadrilateral and point (2, 3) lies inside the quadrilateral
Statement- II Point lies on same side of the lines.
Given the lines y + 2x = 3 and y + 2x = 5 cut the axes at A, B and C, D respectively.
Statement- I ABDC forms quadrilateral and point (2, 3) lies inside the quadrilateral
Statement- II Point lies on same side of the lines.
maths-General
Maths-
The x-coordinates of the vertices of a square of unit area are the roots of the equation  and the y-coordinates of the vertices are the roots of the equation
and the y-coordinates of the vertices are the roots of the equation  then the possible vertices of the square is/are :
then the possible vertices of the square is/are :
therefore the possible vertices of the square are (1,1),(1,2),(2,1),(2,2) and (−1,1),(−1,2),(−2,2),(−2,1)
The x-coordinates of the vertices of a square of unit area are the roots of the equation  and the y-coordinates of the vertices are the roots of the equation
and the y-coordinates of the vertices are the roots of the equation  then the possible vertices of the square is/are :
then the possible vertices of the square is/are :
Maths-General
therefore the possible vertices of the square are (1,1),(1,2),(2,1),(2,2) and (−1,1),(−1,2),(−2,2),(−2,1)
Maths-
The straight lines x + y = 0, 3x + y - 4 = 0 and x + 3y -4 = 0 form a triangle which is
therefore it forms an isosceles triangle
The straight lines x + y = 0, 3x + y - 4 = 0 and x + 3y -4 = 0 form a triangle which is
Maths-General
therefore it forms an isosceles triangle
Maths-
Equation of a straight line passing through the point (4, 5) and equally inclined to the lines 3x = 4y + 7 and 5y = 12x + 6 is
Equation of a straight line passing through the point (4, 5) and equally inclined to the lines 3x = 4y + 7 and 5y = 12x + 6 is
Maths-General
Maths-
If the equation  represents a pair of lines whose slopes are m and
represents a pair of lines whose slopes are m and  , then value(s) of a is/are -
, then value(s) of a is/are -
If the equation  represents a pair of lines whose slopes are m and
represents a pair of lines whose slopes are m and  , then value(s) of a is/are -
, then value(s) of a is/are -
Maths-General
maths-
The curve passing through the points of intersection of  and
and  represents a pair of straight lines which are
represents a pair of straight lines which are
The curve passing through the points of intersection of  and
and  represents a pair of straight lines which are
represents a pair of straight lines which are
maths-General
maths-
The number of divisors of  and
and  are in
are in
The number of divisors of  and
and  are in
are in
maths-General
maths-
The equation of perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points (1, 2) and (–2, 0) is -
The equation of perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining the points (1, 2) and (–2, 0) is -
maths-General
maths-
If  are in
are in
If  are in
are in
maths-General
maths-
An infinite GP has first term  and sum 5, then
and sum 5, then
An infinite GP has first term  and sum 5, then
and sum 5, then
maths-General
maths-
Area of a triangle whose vertices are  is
is
Area of a triangle whose vertices are  is
is
maths-General
maths-
In a geometric progression (GP) the ratio of the sum of the first three terms and first six terms is 125:152 the common ratio is
In a geometric progression (GP) the ratio of the sum of the first three terms and first six terms is 125:152 the common ratio is
maths-General