Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A two eyed man is looking at the junction of two mutually perpendicular mirrors from a far off distance. Assume no reflection to occur from the edge. Then if both the eyes are open

- The eye 1 of man can see image of both eye 1 and eye 2 .
- The eye 1 can see image of eye 1 only and eye 2 see image of eye 2 only.
- The eye 1 can see image of eye 2 only and eye 2 can see image of eye one only.
- All the above statements are false.
The correct answer is: The eye 1 can see image of eye 2 only and eye 2 can see image of eye one only.
Related Questions to study
physics-
A point source of light ' S ' is placed at a distance 10 cm in front of the center of a mirror of width 20 cm suspended vertically on a wall. A man walks with a speed 10 cm/s in front of the mirror at a distance of 20 cm from it as shown in figure. Find the maximum time during which he can see the image of the source S in the mirror.

A point source of light ' S ' is placed at a distance 10 cm in front of the center of a mirror of width 20 cm suspended vertically on a wall. A man walks with a speed 10 cm/s in front of the mirror at a distance of 20 cm from it as shown in figure. Find the maximum time during which he can see the image of the source S in the mirror.

physics-General
physics-
A particle is moving in a circle in front of a plane mirror in the situation as shown in figure. The plane of motion of the particle is perpendicular to the plane of mirror. Then the motion of image of particle with respected to the particle is

A particle is moving in a circle in front of a plane mirror in the situation as shown in figure. The plane of motion of the particle is perpendicular to the plane of mirror. Then the motion of image of particle with respected to the particle is

physics-General
physics-
A plane mirror ' M ' and a concave mirror ' X ' are kept at a separation of 40 an with their reflecting faces facing each other as shown in figure. An object AB is kept perpendicular to the principal axis in position (1). Considering successive reflections first at mirror ' X ' and then at ' M', a real image is formed in front of 'M at a normal distance 8 am form it. If the object is moved to new position (2), the real image is formed at 20 cm from ' M ' with the reflections as described earlier.
Keeping the object in position (1), if the plane mirror is replaced with a convex mirror ' Y ' of focal length 20 m facing the mirror ' X ' after successive reflections first at ' X ' and then at ' Y ', the final image will be

A plane mirror ' M ' and a concave mirror ' X ' are kept at a separation of 40 an with their reflecting faces facing each other as shown in figure. An object AB is kept perpendicular to the principal axis in position (1). Considering successive reflections first at mirror ' X ' and then at ' M', a real image is formed in front of 'M at a normal distance 8 am form it. If the object is moved to new position (2), the real image is formed at 20 cm from ' M ' with the reflections as described earlier.
Keeping the object in position (1), if the plane mirror is replaced with a convex mirror ' Y ' of focal length 20 m facing the mirror ' X ' after successive reflections first at ' X ' and then at ' Y ', the final image will be

physics-General
physics-
In the figure shown consider the first reflection at the plane mirror and second at the convex mirror. AB is object.

In the figure shown consider the first reflection at the plane mirror and second at the convex mirror. AB is object.

physics-General
physics-
A flat mirror M is arranged parallel to a wall Wat a distance 1 from it. The light produced by a point source S kept on the wall is reflected by the mirror and produces a light spot on the wall. The mirror moves with velocity  towards the wall.
towards the wall.

A flat mirror M is arranged parallel to a wall Wat a distance 1 from it. The light produced by a point source S kept on the wall is reflected by the mirror and produces a light spot on the wall. The mirror moves with velocity  towards the wall.
towards the wall.

physics-General
physics-
Figure shows a torch producing a straight light beam falling on a plane mirror at an angle 60°. The reflected beam makes a spot P on the screen along y-axis. If at t=0, the mirror starts rotating about the hinge A with an angular velocity  per second clockwise, find the speed of the spot on screen after time t=15 s.
per second clockwise, find the speed of the spot on screen after time t=15 s.

Figure shows a torch producing a straight light beam falling on a plane mirror at an angle 60°. The reflected beam makes a spot P on the screen along y-axis. If at t=0, the mirror starts rotating about the hinge A with an angular velocity  per second clockwise, find the speed of the spot on screen after time t=15 s.
per second clockwise, find the speed of the spot on screen after time t=15 s.

physics-General
physics-
A ray of light travels from a light source S to an observer after reflection from a plane mirror. If the source rotates in the clockwise direction by 10°, by what angle and in what direction the mirror should be rotated so that the light ray still strikes the deserver?

A ray of light travels from a light source S to an observer after reflection from a plane mirror. If the source rotates in the clockwise direction by 10°, by what angle and in what direction the mirror should be rotated so that the light ray still strikes the deserver?

physics-General
physics-
Two mirrors are inclined at an angle  as shown in the figure. Light ray is incident parallel to one of the mirrors. The ray will start retracting its path after third reflection if:
as shown in the figure. Light ray is incident parallel to one of the mirrors. The ray will start retracting its path after third reflection if:

Two mirrors are inclined at an angle  as shown in the figure. Light ray is incident parallel to one of the mirrors. The ray will start retracting its path after third reflection if:
as shown in the figure. Light ray is incident parallel to one of the mirrors. The ray will start retracting its path after third reflection if:

physics-General
physics-
Two plane mirror AB and AC are inclined at an angle  . A ray of light starting from point P is incident at point Q on the mirror AB, then at R on mirror AC and again at S on AB, finally the ray ST goes parallel to the mirror AC. The angle i which the ray makes with the normal at point Q on mirror AB is
. A ray of light starting from point P is incident at point Q on the mirror AB, then at R on mirror AC and again at S on AB, finally the ray ST goes parallel to the mirror AC. The angle i which the ray makes with the normal at point Q on mirror AB is

Two plane mirror AB and AC are inclined at an angle  . A ray of light starting from point P is incident at point Q on the mirror AB, then at R on mirror AC and again at S on AB, finally the ray ST goes parallel to the mirror AC. The angle i which the ray makes with the normal at point Q on mirror AB is
. A ray of light starting from point P is incident at point Q on the mirror AB, then at R on mirror AC and again at S on AB, finally the ray ST goes parallel to the mirror AC. The angle i which the ray makes with the normal at point Q on mirror AB is

physics-General
physics-
In the figure, the angle between two reflected rays is

In the figure, the angle between two reflected rays is

physics-General
physics-
A ray of light is to travel from point A to point B in figure in the shortest possible time after reflecting from P. Find  .
.

A ray of light is to travel from point A to point B in figure in the shortest possible time after reflecting from P. Find  .
.

physics-General
physics-
Three identical plane mirrors AB, BC, AC are arranged as shown in the figure. Find the total number of images of a point object ' S ' formed by the three mirrors. ( S is at the centre of the system)

Three identical plane mirrors AB, BC, AC are arranged as shown in the figure. Find the total number of images of a point object ' S ' formed by the three mirrors. ( S is at the centre of the system)

physics-General
physics-
A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density  floats in a transparent liquid of density
floats in a transparent liquid of density  kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is  and that of the liquid is
and that of the liquid is  .
.
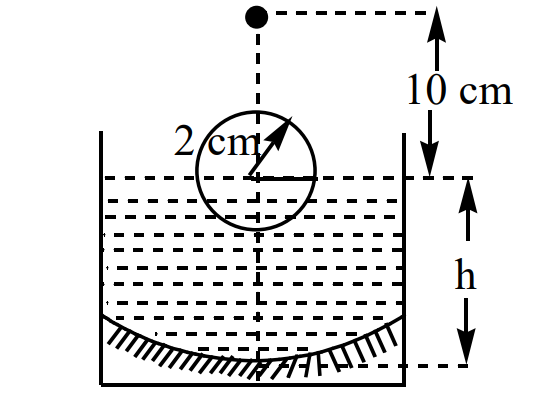
The value of  is (nearly equal to)
is (nearly equal to)
A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density  floats in a transparent liquid of density
floats in a transparent liquid of density  kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is  and that of the liquid is
and that of the liquid is  .
.

The value of  is (nearly equal to)
is (nearly equal to)
physics-General
physics-
A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density  floats in a transparent liquid of density
floats in a transparent liquid of density  kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is  and that of the liquid is
and that of the liquid is  .
.
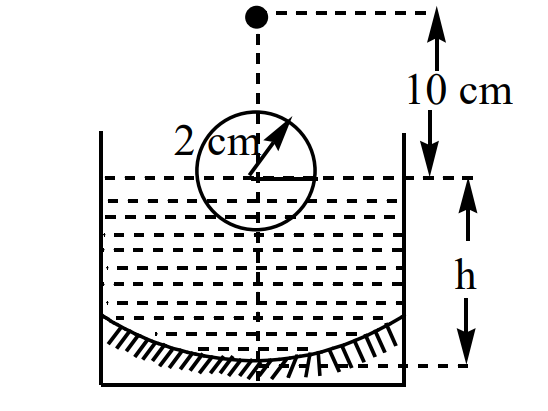
The image formed by the top spherical portion of sphere is (as measured from top of spherical ball)
A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density  floats in a transparent liquid of density
floats in a transparent liquid of density  kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with its radius of anvature 8 cm and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in Fig. When an abject is placed at a distance of 10 cm directly above the centre of the sphere its final image coincide with it. If ' h ' is the height of liquid surface from the apex of the bottom as shown in figure. Consider paraxial rays only for image formation. The refractive index of the sphere is  and that of the liquid is
and that of the liquid is  .
.

The image formed by the top spherical portion of sphere is (as measured from top of spherical ball)
physics-General
physics-
A ray of light is incident normally on one face of  prism of refractive index 5/3 immersed in water of refractive index
prism of refractive index 5/3 immersed in water of refractive index  as shown in figure.
as shown in figure.

A ray of light is incident normally on one face of  prism of refractive index 5/3 immersed in water of refractive index
prism of refractive index 5/3 immersed in water of refractive index  as shown in figure.
as shown in figure.

physics-General



