Physics-
General
Easy
Question
When jet of liquid strikes a fixed or moving surface, it exerts thrust on it due to rate of change of momentum. F = 

If surface is free and starts moving due to thrust of liquid, then at any instant, the above equation gets modified based on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – 

Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :Given cross–section area of jet  velocity of jet
velocity of jet  = 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/
= 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/  , Mass of cart M = 10 kg: The time at which velocity of cart becomes 2m/s, is equal to:
, Mass of cart M = 10 kg: The time at which velocity of cart becomes 2m/s, is equal to:
- 1.6 s
- 2 s
- 3.2 s
- 4s
The correct answer is: 1.6 s
Related Questions to study
physics-
When jet of liquid strikes a fixed or moving surface, it exerts thrust on it due to rate of change of momentum. F = 

If surface is free and starts moving due to thrust of liquid, then at any instant, the above equation gets modified based on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – 

Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :Given cross–section area of jet  velocity of jet
velocity of jet  = 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/
= 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/  , Mass of cart M = 10 kg: In the above problem, what is the acceleration of cart at this instant –
, Mass of cart M = 10 kg: In the above problem, what is the acceleration of cart at this instant –
When jet of liquid strikes a fixed or moving surface, it exerts thrust on it due to rate of change of momentum. F = 

If surface is free and starts moving due to thrust of liquid, then at any instant, the above equation gets modified based on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – 

Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :Given cross–section area of jet  velocity of jet
velocity of jet  = 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/
= 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/  , Mass of cart M = 10 kg: In the above problem, what is the acceleration of cart at this instant –
, Mass of cart M = 10 kg: In the above problem, what is the acceleration of cart at this instant –
physics-General
physics-
When jet of liquid strikes a fixed or moving surface, it exerts thrust on it due to rate of change of momentum. F = 

If surface is free and starts moving due to thrust of liquid, then at any instant, the above equation gets modified based on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – 

Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :Given cross–section area of jet  velocity of jet
velocity of jet  = 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/
= 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/  , Mass of cart M = 10 kg: Velocity of cart at t = 10 s. is equal to:
, Mass of cart M = 10 kg: Velocity of cart at t = 10 s. is equal to:
When jet of liquid strikes a fixed or moving surface, it exerts thrust on it due to rate of change of momentum. F = 

If surface is free and starts moving due to thrust of liquid, then at any instant, the above equation gets modified based on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – 

Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :Given cross–section area of jet  velocity of jet
velocity of jet  = 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/
= 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/  , Mass of cart M = 10 kg: Velocity of cart at t = 10 s. is equal to:
, Mass of cart M = 10 kg: Velocity of cart at t = 10 s. is equal to:
physics-General
physics-
When jet of liquid strikes a fixed or moving surface, it exerts thrust on it due to rate of change of momentum. F = 

If surface is free and starts moving due to thrust of liquid, then at any instant, the above equation gets modified based on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – 

Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :Given cross–section area of jet  velocity of jet
velocity of jet  = 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/
= 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/  , Mass of cart M = 10 kg: Initially (t = 0) the force on the cart is equal to :
, Mass of cart M = 10 kg: Initially (t = 0) the force on the cart is equal to :
When jet of liquid strikes a fixed or moving surface, it exerts thrust on it due to rate of change of momentum. F = 

If surface is free and starts moving due to thrust of liquid, then at any instant, the above equation gets modified based on relative change of momentum with respect to surface. Let any instant the velocity of surface is u, then above equation becomes – 

Based on above concept, in the below given figure, if the cart is frictionless and free to move in horizontal direction, then answer the following :Given cross–section area of jet  velocity of jet
velocity of jet  = 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/
= 10 m/s, density of liquid = 1000 kg/  , Mass of cart M = 10 kg: Initially (t = 0) the force on the cart is equal to :
, Mass of cart M = 10 kg: Initially (t = 0) the force on the cart is equal to :
physics-General
physics-
Statement–I : A block is immersed in a liquid inside a beaker, which is falling freely. Buoyant force acting on block is zero

Statement–II : In case of freely falling liquid there is no pressure difference between any two points
Statement–I : A block is immersed in a liquid inside a beaker, which is falling freely. Buoyant force acting on block is zero

Statement–II : In case of freely falling liquid there is no pressure difference between any two points
physics-General
physics-
Two men ' A' and ' B' are carrying a uniform bar of length ' L' on their shoulders The bar is held horizontally such that A gets one - fourth load If 'A’ is at one end of the bar, the distance of ‘B’ from that end is
Two men ' A' and ' B' are carrying a uniform bar of length ' L' on their shoulders The bar is held horizontally such that A gets one - fourth load If 'A’ is at one end of the bar, the distance of ‘B’ from that end is
physics-General
physics-
Calculate the force ' F 'that is applied horizontally at the axle of the wheel which is necessary to raise the wheel over the obstacle of height 4m Radius of the wheel is 1m and its mass is 10 kg 

Calculate the force ' F 'that is applied horizontally at the axle of the wheel which is necessary to raise the wheel over the obstacle of height 4m Radius of the wheel is 1m and its mass is 10 kg 

physics-General
physics-
A wheel of radius ' r 'and mass 'm' stands in front of a step of height ' h' The least horizontal force which should be applied to the axle of the wheel to allow it to raise onto the step is

A wheel of radius ' r 'and mass 'm' stands in front of a step of height ' h' The least horizontal force which should be applied to the axle of the wheel to allow it to raise onto the step is

physics-General
physics-
A cubical block of side ‘L’ rests on a rough horizontal surface with coefficient of friction A horizontal force F is applied on them' ' block as shown If the coefficient of friction is sufficiently high so that the block does not slide before toppling, the minimum force required to topple the block is

A cubical block of side ‘L’ rests on a rough horizontal surface with coefficient of friction A horizontal force F is applied on them' ' block as shown If the coefficient of friction is sufficiently high so that the block does not slide before toppling, the minimum force required to topple the block is

physics-General
physics-
If the time period of a pendulum is 1 sec, then what is the length of the pendulum at point of  and
and  intersection of graph
intersection of graph

If the time period of a pendulum is 1 sec, then what is the length of the pendulum at point of  and
and  intersection of graph
intersection of graph

physics-General
physics-
The potential energy of a particle of mass 1kg in motion along x-axis is given by  joule, where ' x' is in meter The period of small oscillations in second is
joule, where ' x' is in meter The period of small oscillations in second is
The potential energy of a particle of mass 1kg in motion along x-axis is given by  joule, where ' x' is in meter The period of small oscillations in second is
joule, where ' x' is in meter The period of small oscillations in second is
physics-General
physics-
For the given figure, calculate zero correction.

For the given figure, calculate zero correction.

physics-General
Maths-
If ABCD is a square as shown in the figure then which of the following are adjacent sides ?

If ABCD is a square as shown in the figure then which of the following are adjacent sides ?

Maths-General
Maths-
In the following figure, a pair of adjacent vertices is

In the following figure, a pair of adjacent vertices is

Maths-General
chemistry-
Kinetic theory of gases is a generalization offered by Maxwell, Boltzmann, Clausius, etc., to explain the behavior of ideal gases. This theory assumes that ideal gas molecules neither attract nor repel each other. Average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. A gas equation called kinetic gas equation was derived on the basis of kinetic theory
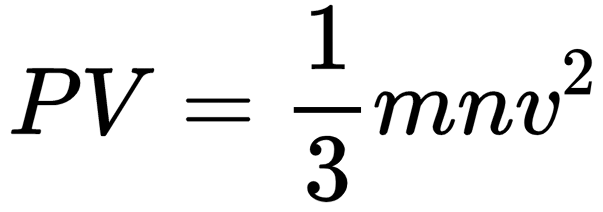

Pick up the correct statement/statements: 1. gas A will tend to lie at the bottom. 2. the number of atoms of various gases A, Band Care same. 3. the gases will diffuse to form homogeneous mixture, 4. average kinetic energy of each gas is same,
Kinetic theory of gases is a generalization offered by Maxwell, Boltzmann, Clausius, etc., to explain the behavior of ideal gases. This theory assumes that ideal gas molecules neither attract nor repel each other. Average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. A gas equation called kinetic gas equation was derived on the basis of kinetic theory
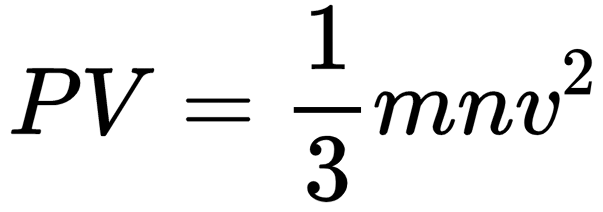

Pick up the correct statement/statements: 1. gas A will tend to lie at the bottom. 2. the number of atoms of various gases A, Band Care same. 3. the gases will diffuse to form homogeneous mixture, 4. average kinetic energy of each gas is same,
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The essential conditions for liquefaction of gases were discovered by Andrews in 1869 as a result of his study of pressure-volume-temperature relationship for  , It was found that above a certain temperature, it was impossible to liquefy a gas whatever the pressure was applied. The temperature below which the gas can be liquefied by the application of pressure alone is called critical temperature
, It was found that above a certain temperature, it was impossible to liquefy a gas whatever the pressure was applied. The temperature below which the gas can be liquefied by the application of pressure alone is called critical temperature  . The pressure required to liquefy a gas at this temperature is called the critical pressure
. The pressure required to liquefy a gas at this temperature is called the critical pressure  The volume occupied by one m91e of the substance at the critical temperature and pressure is called critical volume. Critical constants are related with van der Waals' constant as follows:
The volume occupied by one m91e of the substance at the critical temperature and pressure is called critical volume. Critical constants are related with van der Waals' constant as follows:


Which of the above gases cannot be liquefied at 100 K and 50 - atm?
The essential conditions for liquefaction of gases were discovered by Andrews in 1869 as a result of his study of pressure-volume-temperature relationship for  , It was found that above a certain temperature, it was impossible to liquefy a gas whatever the pressure was applied. The temperature below which the gas can be liquefied by the application of pressure alone is called critical temperature
, It was found that above a certain temperature, it was impossible to liquefy a gas whatever the pressure was applied. The temperature below which the gas can be liquefied by the application of pressure alone is called critical temperature  . The pressure required to liquefy a gas at this temperature is called the critical pressure
. The pressure required to liquefy a gas at this temperature is called the critical pressure  The volume occupied by one m91e of the substance at the critical temperature and pressure is called critical volume. Critical constants are related with van der Waals' constant as follows:
The volume occupied by one m91e of the substance at the critical temperature and pressure is called critical volume. Critical constants are related with van der Waals' constant as follows:


Which of the above gases cannot be liquefied at 100 K and 50 - atm?
chemistry-General



