Maths-
General
Easy
Question
A piece of paper is in the shape of a square of side 1 m long. It is cut at the four corners to make a regular polygon of eight sides (octagon). The area of the polygon is



- None of these
The correct answer is: 
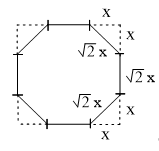
Clearly, So
So
The required area 



Related Questions to study
Maths-
The number of solution of the equation  for
for  is
is
The number of solution of the equation  for
for  is
is
Maths-General
Maths-
The value of  is
is
The value of  is
is
Maths-General
Maths-
In triangle  and
and If
If  is the centre of the circumcircle of triangle
is the centre of the circumcircle of triangle  with radius unity, then the radius of the circumcircle of triangle
with radius unity, then the radius of the circumcircle of triangle  is
is
In triangle  and
and If
If  is the centre of the circumcircle of triangle
is the centre of the circumcircle of triangle  with radius unity, then the radius of the circumcircle of triangle
with radius unity, then the radius of the circumcircle of triangle  is
is
Maths-General
Maths-
If in and
and  then the triangle is
then the triangle is
If in and
and  then the triangle is
then the triangle is
Maths-General
Maths-
The equation  has
has
The equation  has
has
Maths-General
Maths-
If  then
then  is equal to
is equal to
If  then
then  is equal to
is equal to
Maths-General
Maths-
In triangle  if
if  and
and  the sides
the sides  and
and are in
are in
In triangle  if
if  and
and  the sides
the sides  and
and are in
are in
Maths-General
Maths-
Maths-General
Maths-
If the equation  has at least one solution, then the sum of all possible integral values of
has at least one solution, then the sum of all possible integral values of  is equal to
is equal to
If the equation  has at least one solution, then the sum of all possible integral values of
has at least one solution, then the sum of all possible integral values of  is equal to
is equal to
Maths-General
Maths-
Let is equal to
is equal to
Let is equal to
is equal to
Maths-General
Maths-
In any triangle  is always equal to
is always equal to
In any triangle  is always equal to
is always equal to
Maths-General
Maths-
The number of solution of  in
in  is
is
The number of solution of  in
in  is
is
Maths-General
Maths-
The range of  for which the inequality
for which the inequality  is
is
The range of  for which the inequality
for which the inequality  is
is
Maths-General
Maths-
In triangle  , angle
, angle  is greater than angle
is greater than angle  . If the measures of angles
. If the measures of angles  and
and  satisfy the equation
satisfy the equation  , then the measure of angle
, then the measure of angle  is
is
In triangle  , angle
, angle  is greater than angle
is greater than angle  . If the measures of angles
. If the measures of angles  and
and  satisfy the equation
satisfy the equation  , then the measure of angle
, then the measure of angle  is
is
Maths-General
Maths-
In triangle  if angle
if angle  is
is  and area of triangle is 30 sq. units, then the minimum possible value of the hypotenuse
and area of triangle is 30 sq. units, then the minimum possible value of the hypotenuse  is equal to
is equal to
In triangle  if angle
if angle  is
is  and area of triangle is 30 sq. units, then the minimum possible value of the hypotenuse
and area of triangle is 30 sq. units, then the minimum possible value of the hypotenuse  is equal to
is equal to
Maths-General





