Question
In the figure and area
and area The value of
The value of

- 1



The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
In the figure,  , AB = 9 cm, AD = 7 cm, CD = 8 cm and CE = 10 cm Then DE = ?
, AB = 9 cm, AD = 7 cm, CD = 8 cm and CE = 10 cm Then DE = ?

if 2 angles are same in a triangle, then the triangles are similar. we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles.
In the figure,  , AB = 9 cm, AD = 7 cm, CD = 8 cm and CE = 10 cm Then DE = ?
, AB = 9 cm, AD = 7 cm, CD = 8 cm and CE = 10 cm Then DE = ?

if 2 angles are same in a triangle, then the triangles are similar. we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles.
In the figure PR = 6 cm then QR = ? cm
PR = 6 cm then QR = ? cm

we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles
In the figure PR = 6 cm then QR = ? cm
PR = 6 cm then QR = ? cm

we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles
In the figure OB = 2x + 1, OC = 5x – 3, OD = 6x – 5 then AC = ? units.
OB = 2x + 1, OC = 5x – 3, OD = 6x – 5 then AC = ? units.

solving the quadratic equations by the factorization method is used. in this method, the linear term is broken down into 2 terms so that we can take out the common factors from the terms and convert the equation into product form.
In the figure OB = 2x + 1, OC = 5x – 3, OD = 6x – 5 then AC = ? units.
OB = 2x + 1, OC = 5x – 3, OD = 6x – 5 then AC = ? units.

solving the quadratic equations by the factorization method is used. in this method, the linear term is broken down into 2 terms so that we can take out the common factors from the terms and convert the equation into product form.
Two line segments  intersect at E such that
intersect at E such that  If AE = 4cm, BE = 3cm, CE=6cm and DE = x cm then x = ?
If AE = 4cm, BE = 3cm, CE=6cm and DE = x cm then x = ?
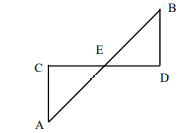
We can also use trigonometry to solve this question since all the angles are same in similar triangles. Angle AEC = angle BED.
Two line segments  intersect at E such that
intersect at E such that  If AE = 4cm, BE = 3cm, CE=6cm and DE = x cm then x = ?
If AE = 4cm, BE = 3cm, CE=6cm and DE = x cm then x = ?

We can also use trigonometry to solve this question since all the angles are same in similar triangles. Angle AEC = angle BED.
From the adjacent figure ,the values of x and y are

From the adjacent figure ,the values of x and y are

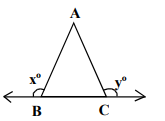
In the given figure, ABC is an Isosceles Triangle in which AB = AC, then

we can also use trigonometry to solve this problem. For the same perpendicular distance from the vertex, the length of side increases with increase in the vertex angle since the perpendicular is the cosine component of the side.
height = side x cos(theta). we know that cosine is a decreasing function. therefore, to keep the height same, the side has to increase.
In the given figure, ABC is an Isosceles Triangle in which AB = AC, then

we can also use trigonometry to solve this problem. For the same perpendicular distance from the vertex, the length of side increases with increase in the vertex angle since the perpendicular is the cosine component of the side.
height = side x cos(theta). we know that cosine is a decreasing function. therefore, to keep the height same, the side has to increase.
In the figure, AB = BC = CD = DE = EF and AF = AE. Then  = ?
= ?
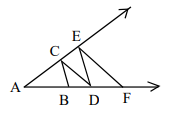
In the figure, AB = BC = CD = DE = EF and AF = AE. Then  = ?
= ?

In the figure, AB = AC,  = 48° and
= 48° and  = 18° . Then
= 18° . Then
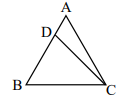
an isosceles triangle is one that has two of its sides equal and the base angles equal to each other.
In the figure, AB = AC,  = 48° and
= 48° and  = 18° . Then
= 18° . Then

an isosceles triangle is one that has two of its sides equal and the base angles equal to each other.
In the figure, ‘x° ’ and ‘y° ’ are two exterior angle measures of  . Then x° + y° is
. Then x° + y° is
if one of the angles were acute then we'd not have been able to conclude whether the sum of the angles were greater than or less than 180 degrees.
In the figure, ‘x° ’ and ‘y° ’ are two exterior angle measures of  . Then x° + y° is
. Then x° + y° is

if one of the angles were acute then we'd not have been able to conclude whether the sum of the angles were greater than or less than 180 degrees.
The perimeter of the following figure is
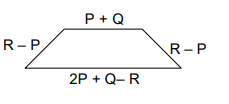
perimeter is the sum of the sides of a polygon.
The perimeter of the following figure is

perimeter is the sum of the sides of a polygon.
Two pupils Ram and Shyam have taken lime water in a vessel, as shown in the figure. Ram is inhaling air from straw A and Shyam is blowing air through straw B. In which case lime water turns milky faster and Why?

Two pupils Ram and Shyam have taken lime water in a vessel, as shown in the figure. Ram is inhaling air from straw A and Shyam is blowing air through straw B. In which case lime water turns milky faster and Why?

If  where
where  then A is equal to
then A is equal to
If  where
where  then A is equal to
then A is equal to
The range of the function 
In this question, we have to find the range of f(x)=. Here solve the function and find when function is at maximum and minimum.
The range of the function 
In this question, we have to find the range of f(x)=. Here solve the function and find when function is at maximum and minimum.





