Question
The magnetic field at the centre of circular loop in the circuit shown below is

The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
Is this quadrilateral a trapezoid?

Is this quadrilateral a trapezoid?

A thin 50 cm long metal bar with mass 750 g rests on, but is not attached to two metallic supports in a uniform 0.45T magnetic field as shown in Fig .A battery and a 25 resistor in series are connceted to the supports. The largest voltage the battery can have without breaking the circuit at the supports (units are in ”V”) is
resistor in series are connceted to the supports. The largest voltage the battery can have without breaking the circuit at the supports (units are in ”V”) is

A thin 50 cm long metal bar with mass 750 g rests on, but is not attached to two metallic supports in a uniform 0.45T magnetic field as shown in Fig .A battery and a 25 resistor in series are connceted to the supports. The largest voltage the battery can have without breaking the circuit at the supports (units are in ”V”) is
resistor in series are connceted to the supports. The largest voltage the battery can have without breaking the circuit at the supports (units are in ”V”) is

What is the area of the trapezoid?

What is the area of the trapezoid?

The radius of a circle is 7 meters. What is area of the circle?

The radius of a circle is 7 meters. What is area of the circle?

Multiply: 9 × 4 =
Multiply: 9 × 4 =
Solve the quadratic equation below using the Quadratic Formula
Solve the quadratic equation below using the Quadratic Formula
In the figure,  If AC = 75 cm AB = 100 cm and BD = 1.25 cm then AD =
If AC = 75 cm AB = 100 cm and BD = 1.25 cm then AD = 
we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles.
In the figure,  If AC = 75 cm AB = 100 cm and BD = 1.25 cm then AD =
If AC = 75 cm AB = 100 cm and BD = 1.25 cm then AD = 
we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles.
we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles.
we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles.
In the figure and area
and area The value of
The value of

In the figure and area
and area The value of
The value of

In the figure,  , AB = 9 cm, AD = 7 cm, CD = 8 cm and CE = 10 cm Then DE = ?
, AB = 9 cm, AD = 7 cm, CD = 8 cm and CE = 10 cm Then DE = ?

if 2 angles are same in a triangle, then the triangles are similar. we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles.
In the figure,  , AB = 9 cm, AD = 7 cm, CD = 8 cm and CE = 10 cm Then DE = ?
, AB = 9 cm, AD = 7 cm, CD = 8 cm and CE = 10 cm Then DE = ?

if 2 angles are same in a triangle, then the triangles are similar. we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles.
In the figure PR = 6 cm then QR = ? cm
PR = 6 cm then QR = ? cm

we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles
In the figure PR = 6 cm then QR = ? cm
PR = 6 cm then QR = ? cm

we can use the property that ratio of sides remains same in similar triangles
In the figure OB = 2x + 1, OC = 5x – 3, OD = 6x – 5 then AC = ? units.
OB = 2x + 1, OC = 5x – 3, OD = 6x – 5 then AC = ? units.

solving the quadratic equations by the factorization method is used. in this method, the linear term is broken down into 2 terms so that we can take out the common factors from the terms and convert the equation into product form.
In the figure OB = 2x + 1, OC = 5x – 3, OD = 6x – 5 then AC = ? units.
OB = 2x + 1, OC = 5x – 3, OD = 6x – 5 then AC = ? units.

solving the quadratic equations by the factorization method is used. in this method, the linear term is broken down into 2 terms so that we can take out the common factors from the terms and convert the equation into product form.
Two line segments  intersect at E such that
intersect at E such that  If AE = 4cm, BE = 3cm, CE=6cm and DE = x cm then x = ?
If AE = 4cm, BE = 3cm, CE=6cm and DE = x cm then x = ?
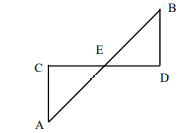
We can also use trigonometry to solve this question since all the angles are same in similar triangles. Angle AEC = angle BED.
Two line segments  intersect at E such that
intersect at E such that  If AE = 4cm, BE = 3cm, CE=6cm and DE = x cm then x = ?
If AE = 4cm, BE = 3cm, CE=6cm and DE = x cm then x = ?

We can also use trigonometry to solve this question since all the angles are same in similar triangles. Angle AEC = angle BED.
From the adjacent figure ,the values of x and y are

From the adjacent figure ,the values of x and y are

In the given figure, ABC is an Isosceles Triangle in which AB = AC, then

we can also use trigonometry to solve this problem. For the same perpendicular distance from the vertex, the length of side increases with increase in the vertex angle since the perpendicular is the cosine component of the side.
height = side x cos(theta). we know that cosine is a decreasing function. therefore, to keep the height same, the side has to increase.
In the given figure, ABC is an Isosceles Triangle in which AB = AC, then

we can also use trigonometry to solve this problem. For the same perpendicular distance from the vertex, the length of side increases with increase in the vertex angle since the perpendicular is the cosine component of the side.
height = side x cos(theta). we know that cosine is a decreasing function. therefore, to keep the height same, the side has to increase.





