Maths-
General
Easy
Question
Number of solutions 
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
The correct answer is: 1
Related Questions to study
Physics-
A tangent galvanometer has a coil of 25 turns and radius of 15 cm. The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field is 3 ´ 10–5 T. The current required to produce a deflection of 45o in it, is
A tangent galvanometer has a coil of 25 turns and radius of 15 cm. The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field is 3 ´ 10–5 T. The current required to produce a deflection of 45o in it, is
Physics-General
Physics-
When  ampere current is passed in a tangent galvanometer, there is a deflection of 30° in it. The deflection obtained when 3 amperes current is passed, is
ampere current is passed in a tangent galvanometer, there is a deflection of 30° in it. The deflection obtained when 3 amperes current is passed, is
When  ampere current is passed in a tangent galvanometer, there is a deflection of 30° in it. The deflection obtained when 3 amperes current is passed, is
ampere current is passed in a tangent galvanometer, there is a deflection of 30° in it. The deflection obtained when 3 amperes current is passed, is
Physics-General
Physics-
The time period of a bar magnet suspended horizontally in the earth's magnetic field and allowed to oscillate
The time period of a bar magnet suspended horizontally in the earth's magnetic field and allowed to oscillate
Physics-General
Physics-
Time period for a magnet is T. If it is divided in four equal parts along its axis and perpendicular to its axis as shown then time period for each part will be

Time period for a magnet is T. If it is divided in four equal parts along its axis and perpendicular to its axis as shown then time period for each part will be

Physics-General
Physics-
At a certain place a magnet makes 30 oscillations per minute. At another place where the magnetic field is double, its time period will be
At a certain place a magnet makes 30 oscillations per minute. At another place where the magnetic field is double, its time period will be
Physics-General
Physics-
At which place, earth's magnetism become horizontal
At which place, earth's magnetism become horizontal
Physics-General
Physics-
At a certain place the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field is B0 and the angle of dip is 45o. The total intensity of the field at that place will be
At a certain place the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field is B0 and the angle of dip is 45o. The total intensity of the field at that place will be
Physics-General
Physics-
At a certain place, the horizontal component  and the vertical component
and the vertical component  of the earth's magnetic field are equal in magnitude. The total intensity at the place will be
of the earth's magnetic field are equal in magnitude. The total intensity at the place will be
At a certain place, the horizontal component  and the vertical component
and the vertical component  of the earth's magnetic field are equal in magnitude. The total intensity at the place will be
of the earth's magnetic field are equal in magnitude. The total intensity at the place will be
Physics-General
Physics-
Lines which represent places of constant angle of dip are called
Lines which represent places of constant angle of dip are called
Physics-General
Physics-
At a place, the horizontal and vertical intensities of earth's magnetic field is 0.30 Gauss and 0.173 Gauss respectively. The angle of dip at this place is
At a place, the horizontal and vertical intensities of earth's magnetic field is 0.30 Gauss and 0.173 Gauss respectively. The angle of dip at this place is
Physics-General
Physics-
The angle of dip is the angle
The angle of dip is the angle
Physics-General
Maths-
If the normal at the points Pi (xi, yi), i = 1 to 4 on the hyperbola xy = c2 are concurrent at the point Q(h, k), then  is equal to
is equal to
If the normal at the points Pi (xi, yi), i = 1 to 4 on the hyperbola xy = c2 are concurrent at the point Q(h, k), then  is equal to
is equal to
Maths-General
Maths-
The most general form of the equation of a conic is given by  . Let x and y-axes be respectively tangent and normal to the conic given by equation ((a) at the origin. Then clearly c = 0. Also by putting y = 0, we get
. Let x and y-axes be respectively tangent and normal to the conic given by equation ((a) at the origin. Then clearly c = 0. Also by putting y = 0, we get  = 0. Both roots of the equation are zero. Therefore g = 0.
= 0. Both roots of the equation are zero. Therefore g = 0.
Hence the most general form of the equation of such a conic is given by .
.
Let foci of the conic represented by the equation , where
, where  and
and  be
be  and
and . Then the feet of perpendiculars from F1 and F2 upon x-axis lie on the curve
. Then the feet of perpendiculars from F1 and F2 upon x-axis lie on the curve
The most general form of the equation of a conic is given by  . Let x and y-axes be respectively tangent and normal to the conic given by equation ((a) at the origin. Then clearly c = 0. Also by putting y = 0, we get
. Let x and y-axes be respectively tangent and normal to the conic given by equation ((a) at the origin. Then clearly c = 0. Also by putting y = 0, we get  = 0. Both roots of the equation are zero. Therefore g = 0.
= 0. Both roots of the equation are zero. Therefore g = 0.
Hence the most general form of the equation of such a conic is given by .
.
Let foci of the conic represented by the equation , where
, where  and
and  be
be  and
and . Then the feet of perpendiculars from F1 and F2 upon x-axis lie on the curve
. Then the feet of perpendiculars from F1 and F2 upon x-axis lie on the curve
Maths-General
Chemistry-
According to Huckel’s rule a compound is said to be aromatic if it contains
According to Huckel’s rule a compound is said to be aromatic if it contains
Chemistry-General
Chemistry-
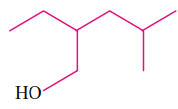 structure is
structure is
 structure is
structure is
Chemistry-General



