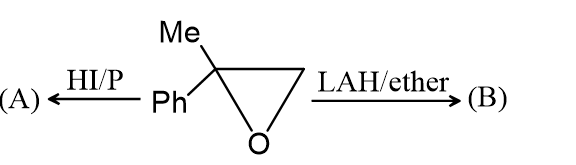Question
In the set up shown in Fig the two slits,  and
and  are not equidistant from the slit S. The central fringe at O is then
are not equidistant from the slit S. The central fringe at O is then

- Always bright
- Always dark
- Either dark or bright depending on the position of S
- Neither dark nor bright.
The correct answer is: Either dark or bright depending on the position of S
Related Questions to study
In a Young’s double slit experimental arrangement shown here, if a mica sheet of thickness t and refractive index  is placed in front of the slit
is placed in front of the slit  then the path difference
then the path difference 

In a Young’s double slit experimental arrangement shown here, if a mica sheet of thickness t and refractive index  is placed in front of the slit
is placed in front of the slit  then the path difference
then the path difference 

 The compound (A) is :
The compound (A) is :
 The compound (A) is :
The compound (A) is :
A) Requires 2 mol of for its saturation
B) Reduces ammoniacal and gives yellow colour with
C) does not reduce Tollens reagent but gives iodoform test
D) n dehydration with conc. gives a mixture of colourless gases
The compound (A) is:
A) Requires 2 mol of for its saturation
B) Reduces ammoniacal and gives yellow colour with
C) does not reduce Tollens reagent but gives iodoform test
D) n dehydration with conc. gives a mixture of colourless gases
The compound (A) is:
 Gives positive Tollens test but negative iodoform test (C) Gives negative Tollens test but positive iodoform test The compound (A) is:
Gives positive Tollens test but negative iodoform test (C) Gives negative Tollens test but positive iodoform test The compound (A) is:
 Gives positive Tollens test but negative iodoform test (C) Gives negative Tollens test but positive iodoform test The compound (A) is:
Gives positive Tollens test but negative iodoform test (C) Gives negative Tollens test but positive iodoform test The compound (A) is:
Redox equations are balanced either by ion-electron method or by oxidation number method. Both methods lead to the correct from of the balanced equation. The ion electron method has two advantages. So some chemists prefer to use the ion-electron method for redox reactions carried out in dilute aqueous solutions, where free ions have more or less independent existence The oxidation state method for redox reactions is mostly used for solid chemicals or for reactions in concentrated acid media For the reaction The -factor is
Redox equations are balanced either by ion-electron method or by oxidation number method. Both methods lead to the correct from of the balanced equation. The ion electron method has two advantages. So some chemists prefer to use the ion-electron method for redox reactions carried out in dilute aqueous solutions, where free ions have more or less independent existence The oxidation state method for redox reactions is mostly used for solid chemicals or for reactions in concentrated acid media For the reaction The -factor is
The valency of carbon is generally 4, but its oxidation state may be -4,-2,0,+2,-1 etc. In the compounds containing C,H, and O, the oxidation number of C is calculated as Oxidation number of Where
and nc are the number of oxygen, hydrogen and carbon atoms , respectively The oxidation state of C in diamond is
The valency of carbon is generally 4, but its oxidation state may be -4,-2,0,+2,-1 etc. In the compounds containing C,H, and O, the oxidation number of C is calculated as Oxidation number of Where
and nc are the number of oxygen, hydrogen and carbon atoms , respectively The oxidation state of C in diamond is
Oxidation reaction involves loss of electrons, and reduction reaction involves gain of electrons. The reaction in which a species disproportionate into two oxidation states (lower and higher) is called disproportionate reaction Which of the following statements is wrong?
Oxidation reaction involves loss of electrons, and reduction reaction involves gain of electrons. The reaction in which a species disproportionate into two oxidation states (lower and higher) is called disproportionate reaction Which of the following statements is wrong?
This section contains five paragraphs. Based on each paragraph, 3-7 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each question has four choices (a) , (b) , (c) , and (d) , out of which only one is correct, except in the paragraph for problem 19-25 Consider the following unbalanced redox reaction:
The oxidation number of X is-2, and neither X nor water is involved in the redox process
The element(s) undergoing oxidation is/are
This section contains five paragraphs. Based on each paragraph, 3-7 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each question has four choices (a) , (b) , (c) , and (d) , out of which only one is correct, except in the paragraph for problem 19-25 Consider the following unbalanced redox reaction:
The oxidation number of X is-2, and neither X nor water is involved in the redox process
The element(s) undergoing oxidation is/are
Statement 1: and
are both bleaching agents
Statement 2:Both are reducing agents
Statement 1: and
are both bleaching agents
Statement 2:Both are reducing agents
Statement 1:Reduction of 3-phenyl prop-2-en-1-al with LAH gives 3-phenyl prpan-1-ol
Statement 2:Both the double bond and the aldehyde group of unsaturated aldehydes are reduced by LAH
Statement 1:Reduction of 3-phenyl prop-2-en-1-al with LAH gives 3-phenyl prpan-1-ol
Statement 2:Both the double bond and the aldehyde group of unsaturated aldehydes are reduced by LAH
Statement 1:A reaction between Fe and I2 occurs, but a reaction between and
does not occur
Statement 2:Fe is a better reducing agent than
Statement 1:A reaction between Fe and I2 occurs, but a reaction between and
does not occur
Statement 2:Fe is a better reducing agent than